|
Atlantic Hurricane Season Sets Records
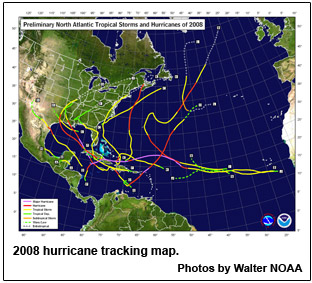
The 2008 Atlantic Hurricane Season officially comes to a close on Sunday, marking the end of a season that produced a record number of consecutive storms to strike the United States and ranks as one of the more active seasons in the 64 years since comprehensive records began.
A total of 16 named storms formed this season, based on an operational estimate by NOAA's National Hurricane Center. The storms included eight hurricanes, five of which were major hurricanes at Category 3 strength or higher. These numbers fall within the ranges predicted in NOAA’s pre- and mid-season outlooks issued in May and August. The August outlook called for 14 to 18 named storms, seven to 10 hurricanes and three to six major hurricanes. An average season has 11 named storms, six hurricanes and two major hurricanes.
“This year’s hurricane season continues the current active hurricane era and is the tenth season to produce above-normal activity in the past 14 years,” said Gerry Bell, Ph.D., lead seasonal hurricane forecaster at NOAA's Climate Prediction Center.
Overall, the season is tied as the fourth most active in terms of named storms (16) and major hurricanes (five), and is tied as the fifth most active in terms of hurricanes (eight) since 1944, which was the first year aircraft missions flew into tropical storms and hurricanes.
For the first time on record, six consecutive tropical cyclones (Dolly, Edouard, Fay, Gustav, Hanna and Ike) made landfall on the U.S. mainland and a record three major hurricanes (Gustav, Ike and Paloma) struck Cuba. This is also the first Atlantic season to have a major hurricane (Category 3) form in five consecutive months (July: Bertha, August: Gustav, September: Ike, October: Omar, November: Paloma).
Bell attributes this year’s above-normal season to conditions that include:
- An ongoing multi-decadal signal. This combination of ocean and atmospheric conditions has spawned increased hurricane activity since 1995.
- Lingering La Niña effects. Although the La Niña that began in the Fall of 2007 ended in June, its influence of light wind shear lingered.
- Warmer tropical Atlantic Ocean temperatures. On average, the tropical Atlantic was about 1.0 degree Fahrenheit above normal during the peak of the season.
NOAA's National Hurricane Center is conducting comprehensive post-event assessments of each named storm of the season. Some of the early noteworthy findings include:
- Bertha was a tropical cyclone for 17 days (July 3-20), making it the longest-lived July storm on record in the Atlantic Basin.
- Fay is the only storm on record to make landfall four times in the state of Florida, and to prompt tropical storm and hurricane watches and warnings for the state’s entire coastline (at various times during its August lifespan).
- Paloma, reaching Category 4 status with top winds of 145 mph, is the second strongest November hurricane on record behind Lenny in 1999 with top winds of 155 mph).
Much of the storm-specific information is based on operational estimates and some changes could be made during the review process that is underway.
“The information we’ll gain by assessing the events from the 2008 hurricane season will help us do an even better job in the future,” said Bill Read, director of NOAA's National Hurricane Center. “With this season behind us, it’s time to prepare for the one that lies ahead.”
NOAA will issue its initial 2009 Atlantic Hurricane Outlook in May, prior to the official start of the season on June 1.
NOAA understands and predicts changes in the Earth's environment, from the depths of the ocean to the surface of the sun, and conserves and manages our coastal and marine resources.
TOP
|